PhD defence of Robin Vallée
Robin Vallée defends his PhD in Physics on March 8, 21
Suspension of inertial particles in turbulent flows.

Robin Vallée completed his thesis within the CFL team, under the direction of Elie Hachem and Jérémie Bec.
Abstract:
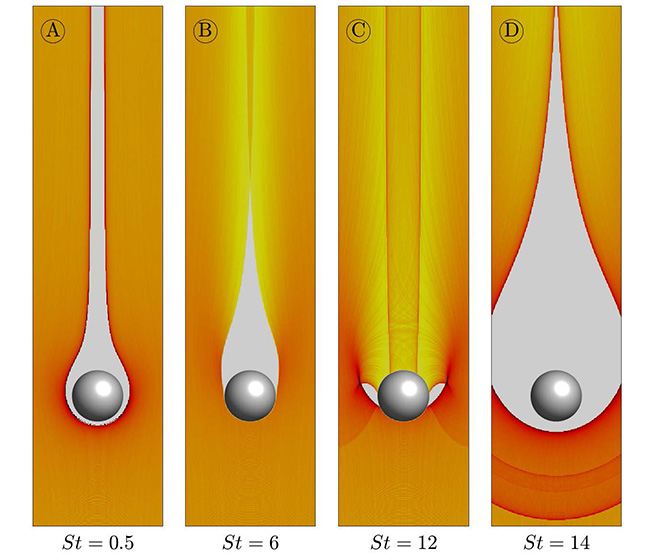
This thesis focuses on the dynamics of inertial particles suspended in turbulent fluid flows that are governed by the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. Understanding the transport of these particles is important in a number of applications, such as the growth of planetesimals by accretion, the evolution of plankton in the oceans, the growth of ice crystals in clouds or the sedimentation of impurities in pipes. Despite the presence of these particles in many industrial or natural processes, their dynamics remain a poorly understood subject. The aim of this thesis is to contribute to a better understanding of certain aspects involving the transport of inertial particles in turbulent flows, using in particular the results of direct numerical simulations. It is divided into four chapters. The first is devoted to an introduction to the motivations, the numerical methods used, as well as to a review of the results already known on this topic. The second chapter deals with the generalization of the phenomenon of turbophoresis in the case of homogeneous and isotropic flows, and therefore completes an approach mainly used for inhomogeneous flows. In particular, it is shown that despite their uniform mean, local turbulent fluctuations lead to inhomogeneities in the distribution of particles at inertial scales. Then, the third chapter is devoted to the accretion of inertial particles by a sphere embedded in a mean _ow. First, it is shown that inelastic bounces of point particles on the surface of the sphere are not sufficient to lead to inelastic collapse, when they are subjected only to a viscous drag force. Secondly, the study of small particles subjected to the force of gravity, shows non-trivial accretion efficiencies, with in particular collisions observed at the back of the collector. Finally, the last chapter deals with particles of finite sizes suspended in a turbulent channel _ow and subject to their viscous drag force and to a lubricating force close to the walls. A statistical study of the distribution of particles and of their collisions with the walls then improves the understanding of deposition mechanisms.
Keywords: Turbulence, inertial particles, accretion, particle-wall interactions, turbophoresis